Hey there, picture this: You’re hauling groceries up three flights of stairs, arms burning but refusing to quit until that last bag hits the counter. Or maybe you’re deadlifting your body weight for the first time, feeling like a superhero who just unlocked a hidden level. That’s muscular strength in action—not some gym bro myth, but the real-deal power that makes everyday life feel effortless. As someone who’s spent over a decade coaching folks from couch potatoes to competitive lifters, I’ve seen how building this foundation changes everything. It’s not about looking like a comic book character; it’s about moving through the world with confidence and zero apologies. Let’s dive in, because trust me, once you get this right, you’ll wonder why you waited so long.
What Is Muscular Strength?
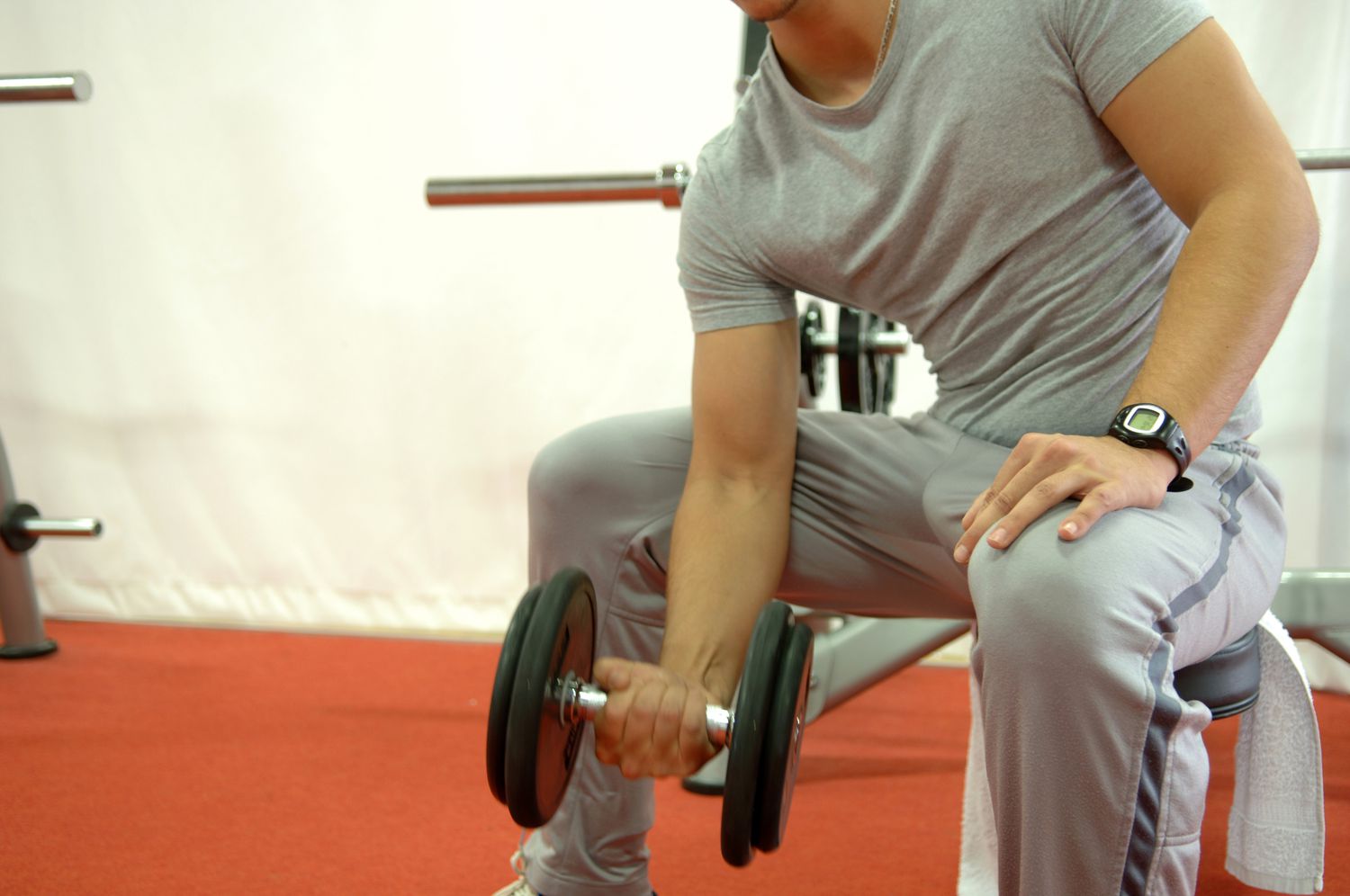
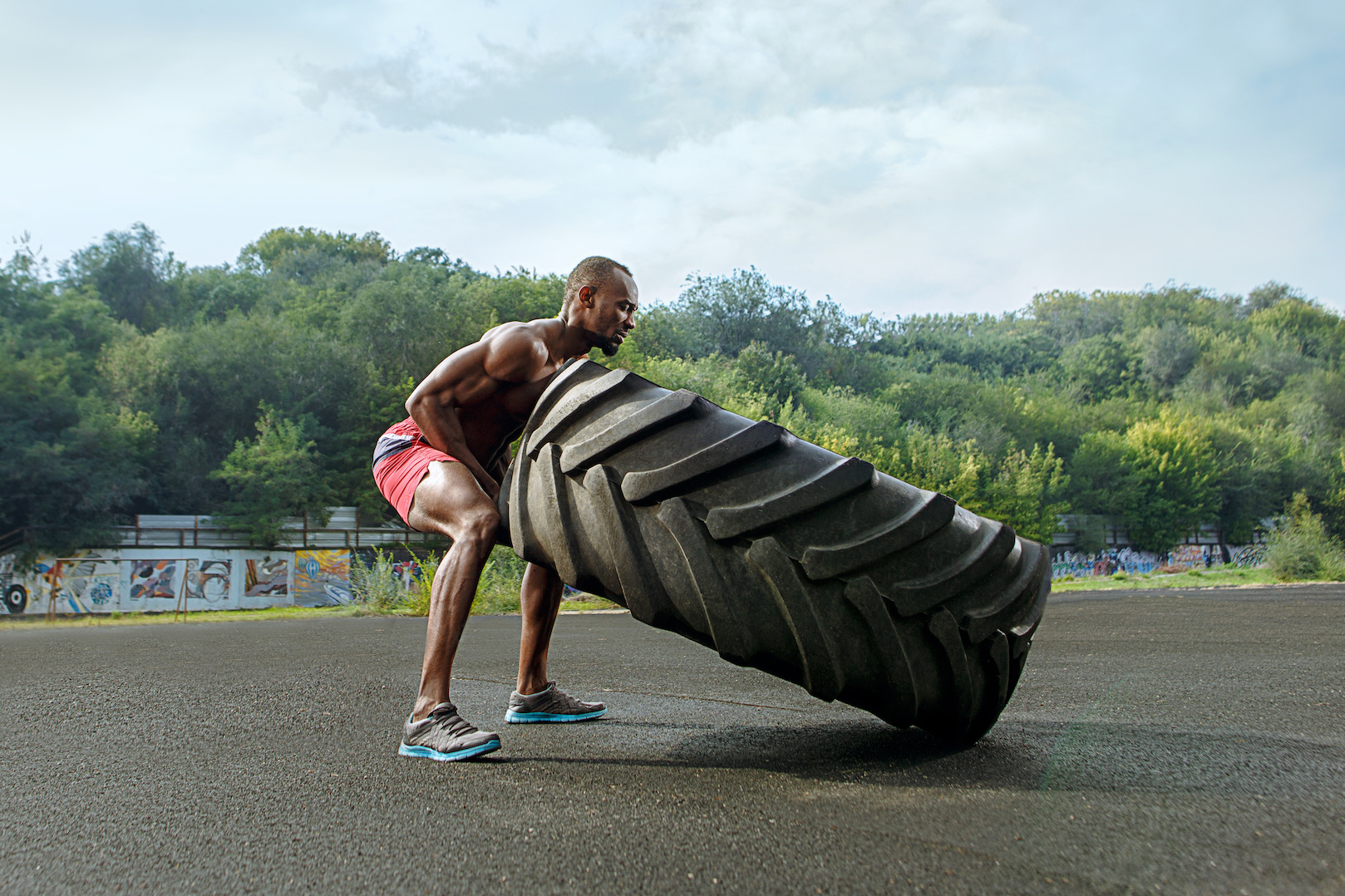
At its core, muscular strength is your body’s ability to generate maximum force from your muscles in a single effort—think hoisting a heavy suitcase into an overhead bin without breaking a sweat. It’s measured by how much weight you can lift or push once, full-out, before tapping out. Unlike endurance, which is about going the distance, strength is that explosive “one and done” punch.
This isn’t just gym lingo; it’s backed by sports science pros who define it as the peak tension your skeletal muscles can produce against resistance. I remember my first real strength test: a 1-rep max bench press that left me grinning like an idiot. It wasn’t pretty, but it showed me what my body could do when pushed.
Why does it matter? Because in real life, strength keeps you independent—lifting kids, gardening without strain, or just chasing joy without hesitation.
The Science Behind Muscular Strength
Your muscles aren’t magic; they’re a symphony of fast-twitch fibers firing like pistons under neural commands from your brain. When you train strength, you’re beefing up those type II fibers, increasing cross-sectional area for more force output, and sharpening neuromuscular efficiency so every signal hits harder.
Research from places like the American College of Sports Medicine highlights how resistance training boosts hormone responses—like testosterone and growth hormone—that repair and thicken muscle tissue. It’s not overnight; expect 5-10 weeks for noticeable gains, but oh boy, the payoff.
I’ve coached a 50-year-old dad who started with empty barbells; six months in, he was pressing 135 pounds, crediting it for reclaiming his weekends with the grandkids. Science meets sweat, and suddenly, you’re unstoppable.
Benefits of Building Muscular Strength
Strength training isn’t vanity—it’s vitality. It torches calories even at rest, sculpts a leaner body comp by swapping fat for muscle, and fortifies bones against osteoporosis. Mentally? It sharpens focus, eases anxiety, and delivers that post-lift high-endorphin buzz.
For aging gracefully, it’s gold: Studies show it slashes fall risk by 30% and keeps joints stable. Plus, who doesn’t love clothes fitting better?
In my early 20s, I ignored strength for endless cardio; I was skinny-tired. Switching gears added pep to my step and a spark to my mood. It’s the quiet confidence of knowing you can handle whatever life throws.
Health Benefits
Strong muscles mean better insulin sensitivity, lower blood pressure, and a revved metabolism that fights off type 2 diabetes. Heart health gets a win too, as strength work complements cardio for overall endurance.
Emotionally, it builds resilience—lifting heavy mirrors tackling tough days. One client, post-divorce, found therapy in the barbell; her lifts rose as her spirits did.
Performance Benefits
Athletes, listen up: Strength underpins speed, power, and injury-proofing. Runners shave seconds off PRs; cyclists climb hills easier.
I’ve seen weekend warriors transform— a soccer mom deadlifting her weight now dominates pickup games. It’s that edge where effort meets ease.
Muscular Strength vs. Muscular Endurance: Key Differences
Strength is the sprint—max force in one burst—while endurance is the marathon, sustaining lighter loads over reps or time. Strength builds via heavy lifts (3-5 reps); endurance via circuits (15+ reps).
Both matter, but confuse them and you’ll plateau. A powerlifter crushes one heavy squat; a hiker endures miles of moderate steps.
Early in my career, I chased endurance vibes in strength sessions—endless light sets. Flop. Balancing them unlocked real progress.
Comparison Table: Strength vs. Endurance
| Aspect | Muscular Strength | Muscular Endurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Max force in single contraction | Repeated contractions over time |
| Training Reps | 1-6 reps, heavy loads | 12+ reps, lighter loads |
| Rest Between Sets | 3-5 minutes | 30-90 seconds |
| Primary Benefit | Power, bone density | Stamina, fatigue resistance |
| Example Exercise | Deadlift (heavy) | Push-ups (high volume) |
This table’s your cheat sheet—use it to tweak workouts without guesswork.
How to Measure Your Muscular Strength
Start simple: Test your one-rep max (1RM) on big moves like squats or bench presses. Warm up, then load progressively until you hit your limit—safely, with a spotter.
No gym? Bodyweight tests: How many full push-ups in a row? Track monthly to spot gains.
I test clients quarterly; it’s motivating to see numbers climb. Pro tip: Use apps like Strong for logging—keeps it fun, not frantic.
Common Testing Methods
- 1RM Testing: Gold standard for force output, but ease in if new.
- 3-5RM Estimates: Safer for beginners; plug into calculators for 1RM approx.
- Functional Tests: Timed wall sits or grip holds for real-world vibes.
Remember my first 1RM? Nerves had me shaking— but nailing it built trust in my training.
Top Exercises to Build Muscular Strength
Compound lifts rule: They hit multiple muscles, max efficiency. Aim for 3-4 sets of 4-6 reps, heavy but form-perfect.
Mix free weights, machines, and bodyweight for variety. Beginners, start light—ego’s the real enemy here.
One foggy morning run turned gym session hooked me on squats; that full-body burn? Addictive.
Lower Body Exercises
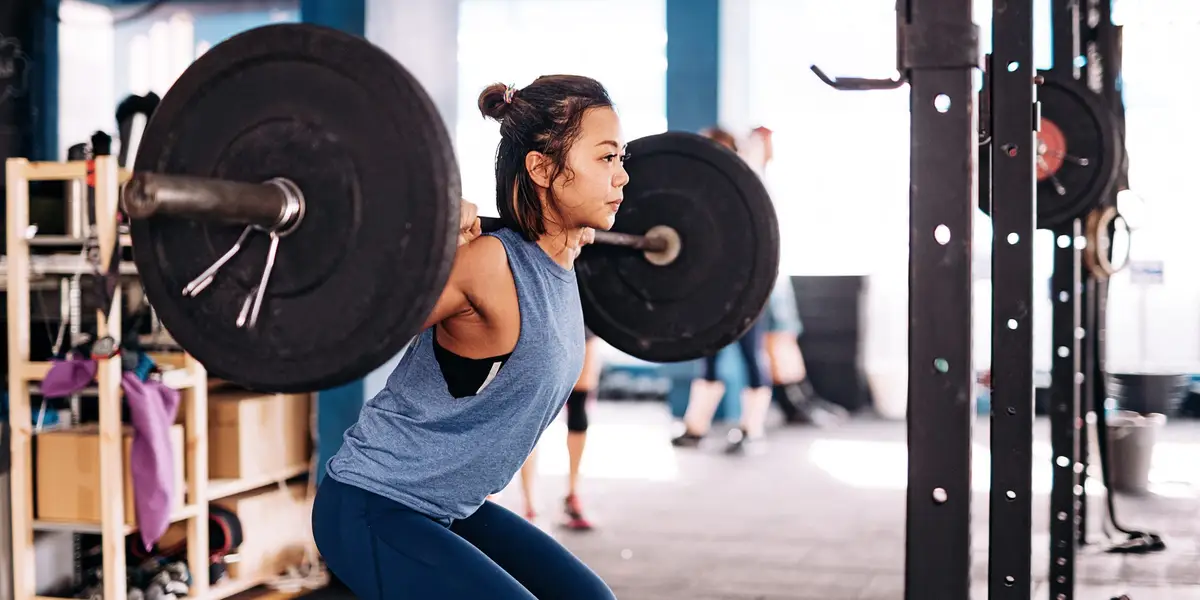
- Squats: Back or goblet—build quads, glutes, core. Feet shoulder-width, descend till thighs parallel.
- Deadlifts: Conventional or Romanian; hinge at hips, lift from ground. Powerhouse for posterior chain.
- Lunges: Walking or reverse; step forward, drop till back knee hovers. Unilateral magic for balance.
These aren’t fluff—they’re your ticket to stairs without groans.
Upper Body Exercises
- Bench Press: Barbell or dumbbell; press from chest to lockout. Chest, tris, shoulders unite.
- Pull-Ups: Assisted if needed; pull chin over bar. Back and biceps builder extraordinaire.
- Overhead Press: Standing military; push bar from shoulders skyward. Delts and stability soar.
I once bet a buddy I couldn’t strict-pull 10; training paid off with bragging rights and broader lats.
Core and Full-Body Moves
- Planks: Hold forearm position; engage everything. Not flashy, but foundational.
- Farmer’s Carries: Walk with heavy dumbbells; grip, posture, total-body tension.
- Turkish Get-Ups: Kettlebell from lie to stand; coordination and strength in spades.
Core’s the glue—skip it, and your lifts leak power.
Designing a Muscular Strength Training Program
Craft a plan: 2-3 sessions weekly, full-body or split (push/pull/legs). Progressive overload—add weight/reps weekly—drives gains.
Warm up dynamically, cool with stretches. Fuel with protein post-workout; sleep’s your secret sauce.
My go-to newbie program: Three days, big lifts only. Simple, sustainable—results in weeks.
Beginner Program: 4-Week Starter
| Week | Exercise | Sets x Reps | Rest |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-2 | Squat | 3×6 | 2 min |
| Bench | 3×6 | 2 min | |
| Rows | 3×6 | 2 min | |
| 3-4 | Add 5-10lbs | 3×5 | 3 min |
Build slow; celebrate small wins. It’s progress, not perfection.
Pros and Cons of Strength Training
Pros:
- Boosts metabolism for easier fat loss.
- Enhances posture, reducing back pain.
- Improves mental toughness—life’s reps get easier.
Cons:
- Risk of injury if form slips (hence, learn proper!).
- Time commitment; start small to stick.
- Soreness newbie phase—ice baths help, promise.
Humor alert: That first DOMS? Feels like you wrestled a bear. Spoiler: You win eventually.
Nutrition and Recovery for Optimal Gains
Fuel like a machine: 1.6-2.2g protein/kg bodyweight daily—eggs, chicken, beans. Carbs for energy, fats for hormones.
Recovery? Sleep 7-9 hours; active rest days. Foam roll, walk it out.
Post-knee injury, I dialed nutrition—collagen shakes, balanced macros. Healed faster, lifted smarter.
Essential Recovery Tools
- Foam Roller: Self-massage for knots; 10 mins daily.
- Sleep Tracker Apps: Prioritize Zzz’s; they’re 50% of gains.
- Epsom Salts Baths: Soothe muscles, unwind like a boss.
Where to snag these? Amazon for rollers, or hit REI for quality gear.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Rushing form for weight? Recipe for tweaks. Mirror check or film yourself—brutal honesty pays.
Skipping warm-ups? Cold muscles snap. 5-10 mins light cardio, dynamic swings.
Overtraining without rest? Burnout city. Listen to your body; deload every 4-6 weeks.
I once ego-lifted a deadlift—strained back for weeks. Lesson: Patience over pride.
Quick Fixes for Pitfalls
- Bad Form? Hire a trainer; apps like Form Check help too.
- Plateaus? Switch exercises; periodize with waves of heavy/light.
- Boredom? Add music, buddies—fun fuels consistency.
People Also Ask (PAA)
Ever Googled and seen those sneaky side questions? Here’s the real talk on what folks wonder most about muscular strength.
What is the difference between muscular strength and muscular endurance?
Strength is max effort once—like a single heavy lift—while endurance is repeating moderate efforts, say 20 push-ups without crumbling. Both shine in life: Strength for bursts, endurance for longevity. Balance them for all-around fitness.
How often should I do strength training?
Twice a week hits the sweet spot for beginners, ramping to three as you adapt. Full-body sessions keep it simple. I train three days; any more, and recovery rebels.
Can strength training help with weight loss?
Absolutely—it ramps your resting burn by adding muscle, which guzzles calories. Pair with cardio for fat-melt magic. One client dropped 15 pounds, crediting squats over salads.
Is strength training safe for older adults?
Yes, if progressed smartly. It combats sarcopenia (age-related muscle loss) and boosts balance. Start light; consult docs. My 65-year-old mentee now hikes weekly—stronger than her 40s.
What are the best tools for home strength training?
Dumbbells, resistance bands, and a pull-up bar top the list—versatile, affordable. Bowflex SelectTech adjustable sets save space. Bodyweight’s free entry.
FAQ
Got lingering Qs? These pop up in sessions all the time—straight answers, no fluff.
How long does it take to see muscular strength gains?
Four to eight weeks for newbies, with consistent training and eats. Track lifts, not mirror—patience pays. I felt it at week three; full transformation by month two.
Can women build as much strength as men?
Heck yes, relative to body size. Hormones differ, but gains are real—strong women lift worlds. My female clients outpace dudes in form and fire.
What’s the best way to start strength training at home?
Bodyweight basics: Squats, push-ups, planks. Add bands for progression. Free YouTube channels like Athlean-X guide you gold.
Does strength training increase height?
No, post-puberty—it’s bone, not muscle magic. But better posture makes you appear taller. Bonus: Confidence adds inches.
How do I know if I’m overtraining my muscles?
Signs: Lingering soreness, stalled lifts, irritability. Rest up; it’s not weakness. I’ve hit walls—deloads turned them to wins.
There you have it—your roadmap to muscular might. Start small, stay consistent, and watch life lift lighter. What’s your first move? Drop a comment; let’s chat gains. You’ve got this.







Leave a Reply